
What is varicose veins and how does it appear? What if you do not treat varicose veins and how to prevent it? We talk about the complications of varicose veins, explain in detail why trophic ulcers appear and why compression stockings are needed.
What is varicose veins and how does it appear?
The veins have special valves that prevent blood from flowing through the blood vessels. But with varicose veins, these valves do not close completely - blood collects in the vein and stretches it.
Symptoms of varicose veins in the early stages:
- The veins in the legs become brighter, more visible;
- On the inner surface of the legs and thighs, varicose joints begin to appear;
- If you stand, sit or walk for a long time, there is heaviness in the legs, feeling of satiety (most often in the evening, in calves);
- At the sites of varicose veins, aches or sharp pains appear, in the evening and at night - cramps in the calf muscles;
- The legs are very swollen by the end of the day, but in the morning the swelling disappears.
Important!
Already at this stage it is necessary to consult a doctor.
With progression, varicose veins become chronic (chronic venous insufficiency). Symptoms:
- Intradermal veins appear with strong dark blue curves: they protrude above the surface of the feet and legs, look like bunches of overripe red grapes;
- There is arched pain in the legs and calves, a feeling of heat in the legs, cramps at night in the calf muscles, strong swelling;
- The skin becomes dry, pigmentation appears, it becomes darker, brown spots appear.
Important!
Do not start the disease! With varicose veins, tissue nutrition is interrupted. There is not enough food for the vessels and the skin - sores, eczema and even ulcers appear, which heal very poorly.
Treatment of varicose veins
There are two ways to treat varicose veins: conservative and surgical.
- Conservatives: compression therapy. The compression underwear squeezes the affected leg - the diameter of the superficial veins is reduced, the proper pressure in the vein is restored. Blood flow decreases, vessel walls remain in good shape, valves close, blood does not stagnate and circulate well, the speed of blood movement through deep veins increases. Stagnant blood volume is reduced, lymphatic flow is improved.
- In advanced cases, when conservative treatment does not help, the doctor will suggest a surgical route: remove the varicose veins, remove the affected veins. To restore functions, deflections are set or valve mobility is restored so that its valves close.
Compression knitwear for varicose veins and ulcers
Compression stockings are special socks that fit well on the bottom of the foot and become looser as they rise to the thighs. This improves blood circulation and stimulates blood flow from the lower extremities to the heart.
Compression stockings are chosen individually, so consult a phlebologist first: you can not choose the socks yourself.
The phlebologist will look at the tone of the vein, in which particular valve there is a problem with the valves not closing. The problem may be, for example, in the thighs: then you have to wear compression stockings. If there is a problem with closing the valve below the knee, then socks or stockings are chosen.
Important!
For maximum efficiency, compression stockings should be worn at all times - removed only before bedtime.
How to wear compression stockings?
- Once you wake up, place your feet on the wall and lie down like that for a while - so that the blood flows as much as possible to the hips;
- Without getting up, wear compression stockings.
In this position (lying down, legs raised), blood circulation is equal, blood does not stagnate. When the compression stockings are on the feet, the veins are in good shape and the valves close tightly and push the blood further through the vessels.
What happens if varicose veins are not treated?
If you do not start treating varicose veins in time, life-threatening complications can occur:
Thrombophlebitis- inflammation of the vein due to the formation of blood clots in it. Symptoms:
- redness;
- the place where the thrombus is located becomes hot;
- an inflamed vein hurts a lot.
If treatment is started on time, the thrombus will stop growing. Residual blood clots can settle for a long time - sometimes months. If not treated or done incorrectly, the clot can increase.
Pulmonary emboli.The thrombus manifested by thrombophlebitis detaches from the wall of the blood vessels in the leg and leaves with the bloodstream. It blocks the pulmonary artery or its branches - this is fatal. Unfortunately, even after having long suspected this complication, doctors can do nothing about it.
Symptoms:
- chest pain;
- accelerated heartbeat;
- dyspnea;
- unreasonable anxiety and unreasonable feeling of fear.
Deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities. This is a serious and dangerous complication of varicose veins. The internal veins are blocked, because of this, the blood flow is almost completely stopped - all the tissues of the foot do not receive food and it turns blue.
Venous gangrene of the extremities- severe deep vein thrombosis, in which there is no nutrition of the limbs, arterial blood flow is disturbed. Due to the fact that blood does not flow, gangrene is formed: the foot, in fact, dies - starting from the toes.
Trophic ulcer- long-term non-healing ulcers that appear due to tissue malnutrition. Lymph gets stuck in the lymphatic vessels, they experience a large load and can not withstand the amount of lymph. Therefore, lymph droplets begin to appear in the eye through the skin. Because of this, the epidermis begins to bloom - an ulcer with dense ragged edges forms. Every touch on it causes severe pain.
Bacteria develop rapidly in ulcers: an infection joins, a bleeding ulcer begins to irritate. This can lead to very serious complications, including blood poisoning.
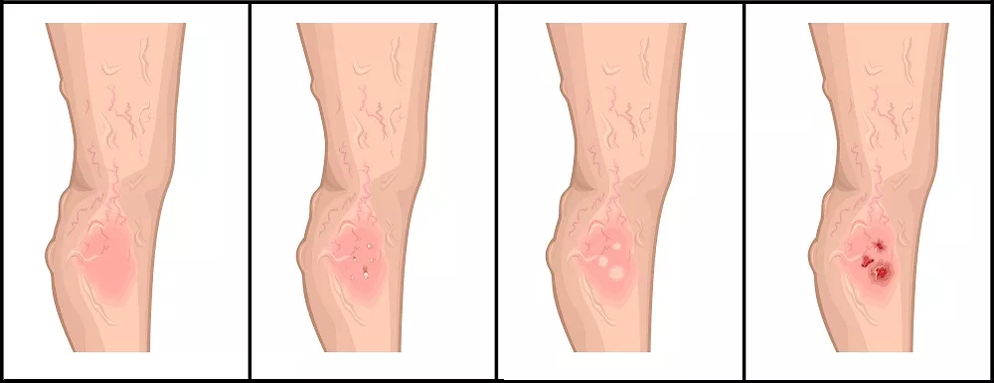
Trophic ulcers are of two types:
- venous, when the subcutaneous and deep veins of the limbs are affected;
- arterial, when the arteries in the legs are affected and the natural nutrition of the limbs is disrupted.
Treatment of trophic ulcers
Trophic ulcers are treated with elastic compression, medications, physiotherapy and surgery.
Caring for trophic ulcer involves four stages.
The first stage - antiseptics
- Antiseptic solution for wound treatment. It is applied to the surface of a trophic ulcer, if cavities have formed under the skin, they are also filled with gel.
- The gel, which has an antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect, improves microcirculation, reduces redness and swelling of the skin, reduces pain, relieves itching and slipping of the skin, blocks the spread of infection and prevents the appearance of teeth.
- An aqueous solution of a halogen or benzyldimethyl-myristoylamino-propylammonium group antiseptic.
The second stage - gel to soften dead tissue
Dead tissue is necrosis: black tissue hardened on the surface of the ulcer. If not removed, the ulcer will not heal. To do this, the necrosis is first softened. This is done using special gel.
The third stage is the formation of an optimal environment for wound healing
Healing is facilitated by creating a moist environment on the wound. If there is no necrosis, use compresses for quick healing. Here are some bandages that will fit:
Alginate coating:
- An alginate dressing that turns into a soft gel upon contact with wound secretions, providing optimal conditions for wet wound healing;
- A dressing that fills the wound cavity and creates a microenvironment that promotes rapid healing;
- Sponge bandage with hydrogel layer. Its structure absorbs secretions and maintains a moist environment in the wound;
- Alginate sponge coating composed of calcium and hydrocolloid alginates;
- Sterile self-absorbing sodium alginate-based dressing, which is suitable for wounds and burns, accelerates healing;
- Hydroactive dressing for deep wounds. Cleanses the wound, accelerates its healing, maintains an optimal environment in the wound for up to three days without changing the dressing.
Sponge bandages:
- Double-sided foam bandage. Protects the wound, absorbs leaks from the wound, creates an optimal water balance in the wound;
- Hydrophilic polyurethane sponge coating;
- A dressing with a complex of enzymes and chitosan is suitable for infected wounds (if there is pus in the wound);
- A spongy antimicrobial dressing, consisting of a polyurethane sponge coating and a silver alginate matrix.
The fourth stage - wound healing
When the wound is cleansed and an optimal environment is created in it, it begins to heal, the edges of the wound shrink. For safe and fast healing, use special clothing.
Mesh oil bandages:
- A Peruvian balm oil sauce applied when fresh skin appears on the wound;
- Dressing with triglyceride-based ointment, which promotes healing and cares for the edges of the wound;
- The bandage, which looks like a square of wax, is soft and quite dense. It can stay in the wound for up to seven days;
Film dressings that can be used to fix dressings to wounds:
- Film bandage (but breathable) against water, protects the wound from microorganisms. Can be used to adjust previous bandages and as a standalone bandage.
- Polyurethane bandage with transparent film, the skin under it does not sweat, breathes.
Important!
These dressings are suitable for healing not only trophic ulcers, but also for any wound that heals long.
Prevention of varicose veins
- Exercise as much as possible: the more you move, the better the blood circulation in the veins;
- Give up bad habits;
- Contact a phlebologist in time at the first symptoms of the disease;
- Periodically do an ultrasound of the vessels - the doctor will notice the first changes;
- After a day at work, return home and lie with your feet on the wall for about 15 minutes.
Prevention of trophic ulcers
- Watch your weight: puts pressure on your legs, loads the vascular and lymphatic system. If necessary, follow the diet;
- Walk as often as possible;
- If possible, raise your legs, keeping them in an upright position as often as possible. In the evening, you can lie down on the sofa and raise your legs, placing them on the wall: you should lie down like this for at least 15 minutes;
- Treat the veins of the lower extremities in time;
- Quit smoking - greatly reduces the blood supply to the tissues and contributes to the development of trophic ulcers;
- Take care of your feet: wear appropriate shoes so that they do not sting or rub;
- Check your feet regularly: check the color of the skin on your feet. If the feet turn blue in the evening and the veins are visible in the feet, contact a phlebologist;
- Moisturize the skin with emollient, moisturizing, nourishing creams;
- Keep your feet warm, dress for the weather;
- Try not to damage the skin.


















